Drug Transport
Human Efflux Model
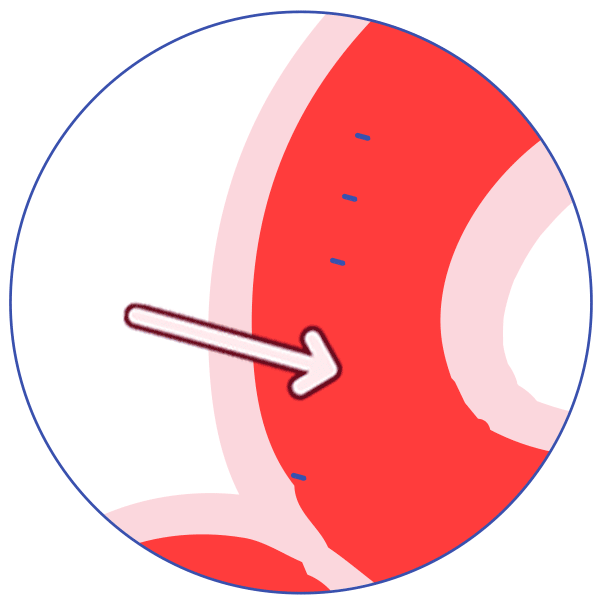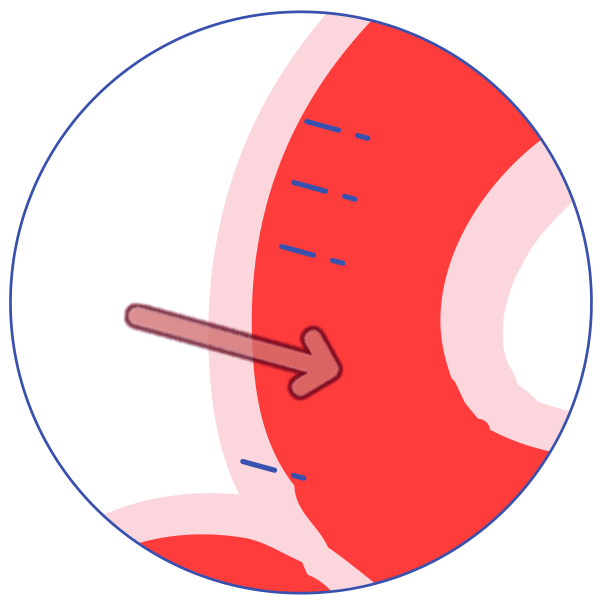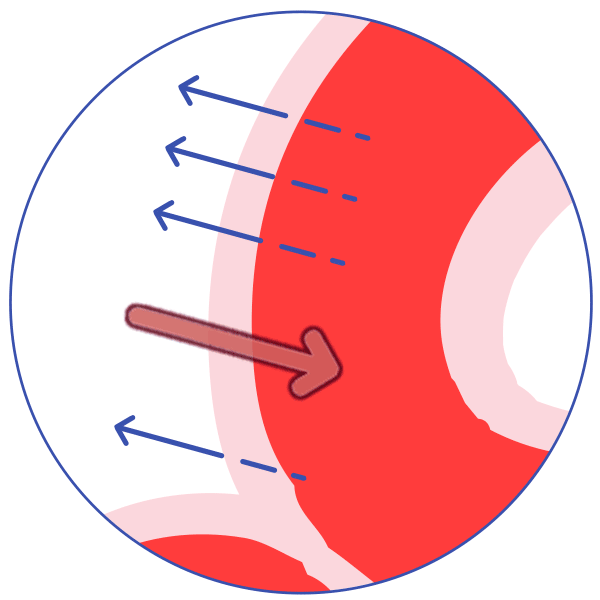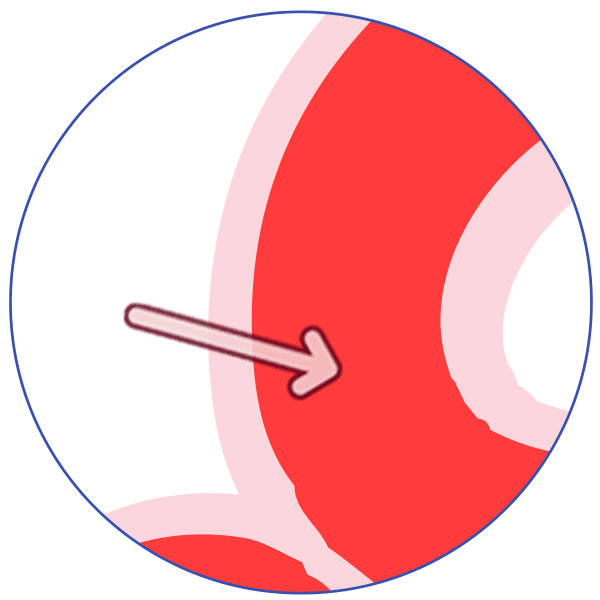
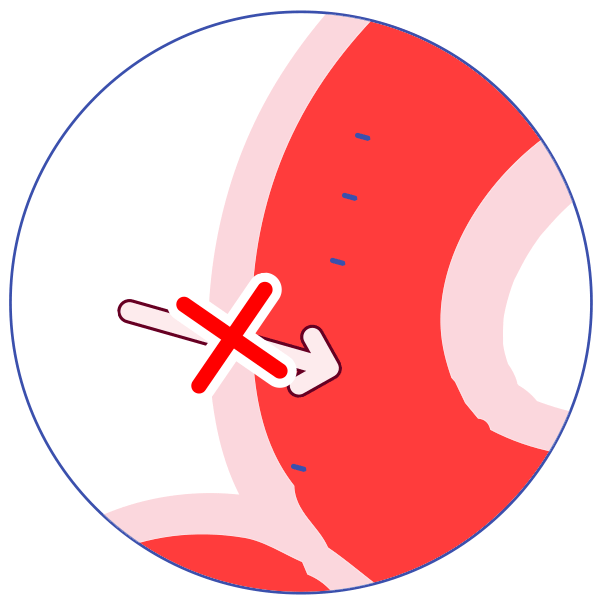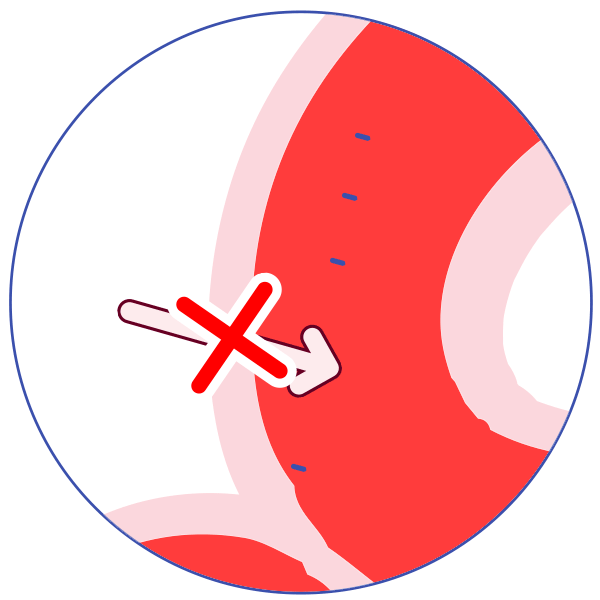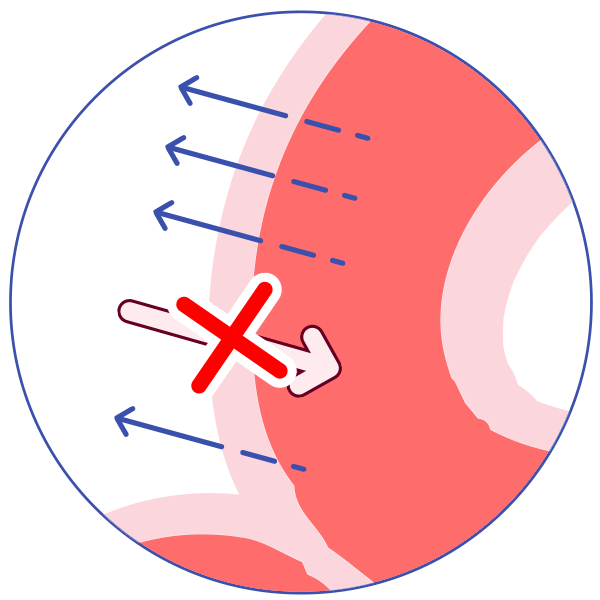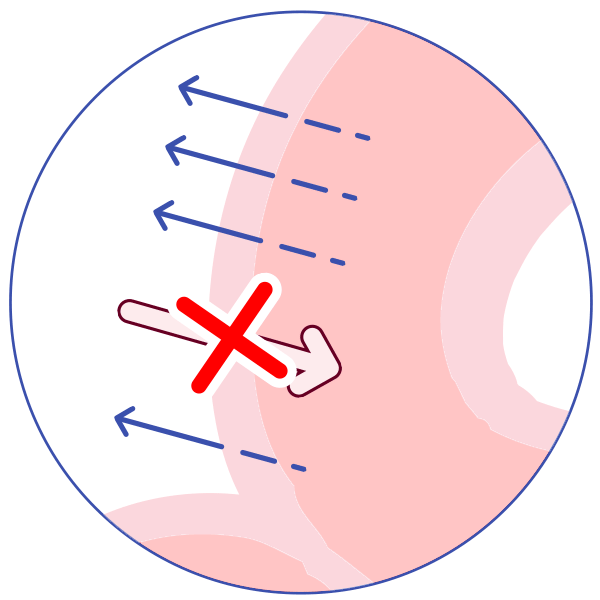
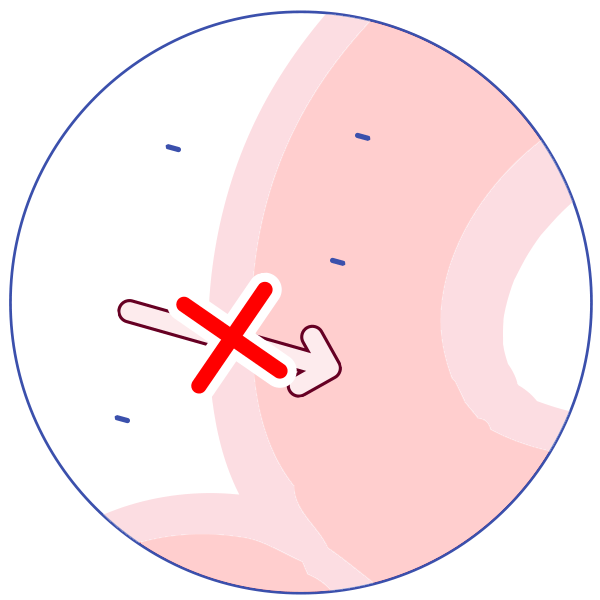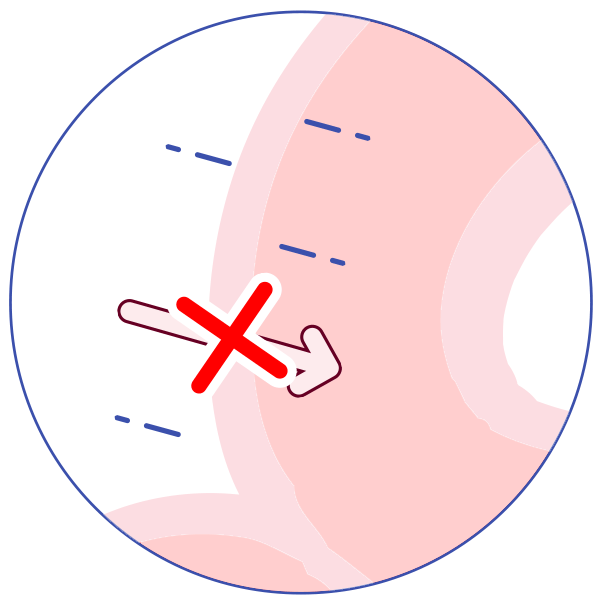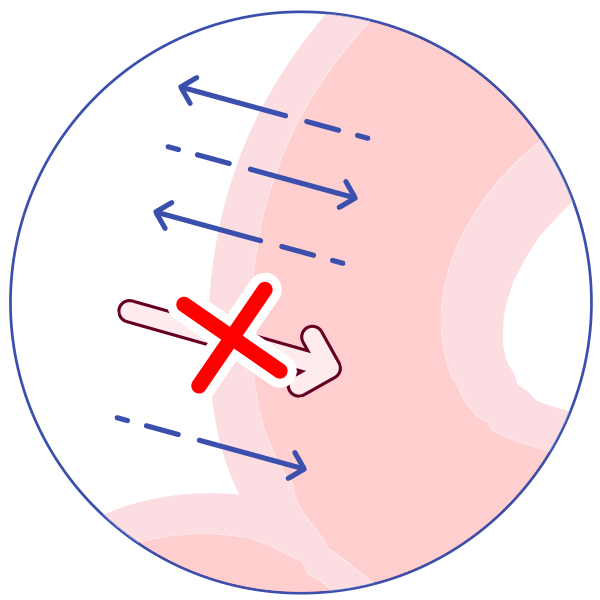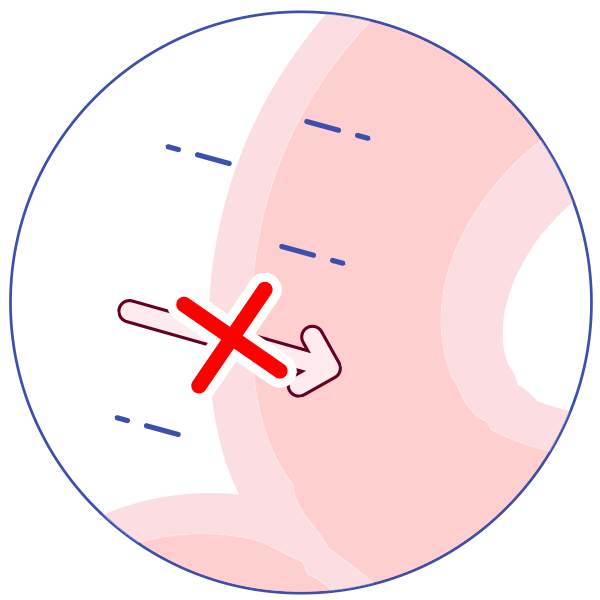
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is an active transporter that protects the body from some harmful substances (including some drugs) by transporting the substance out of the body or out of sensitive organs. Examples:
It transports drugs back out of the gut wall into the gut lumen, thus reducing absorption!
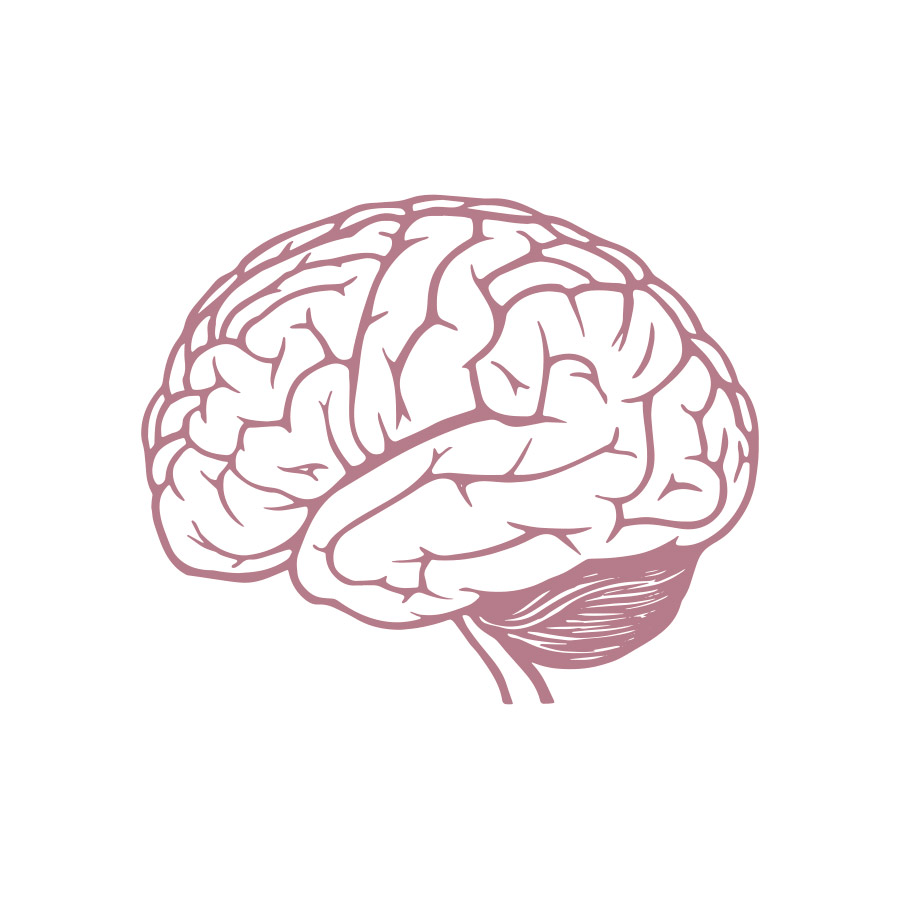
It helps keep some drugs out of the brain.
It transports drugs out of the kidney into the urine. Some drugs inhibit P-glycoprotein, allowing more of the first drug to be absorbed and less to be excreted, and allowing more of the drug to reach organs such as the brain.














Stomach
Small Intestine
P-glycoprotein
P-glycoprotein
Diffusion
Brain
P-glycoprotein
Diffusion
Kidney
P-glycoprotein